Probably the most common kind of way of issuing and registering new stocks is a shelf registration. This is filed on SEC Form S-3 (F-3 if the issuer is a foreign company). These can be used with multiple types of offerings, including most commonly PIPEs, Private Investments in Public Equities, where the shares have been sold to an investor and the shares are now being registered so that investor can sell those shares; ATMs or At the Market Offerings (PDF), where a company sells shares into the open market from time to time; and registration of shares underlying warrants or convertible bonds.
Shelf Takedowns by Greenberg Traurig (PDF)
FAQs about Shelf Offerings by Morrison Foerster (PDF)
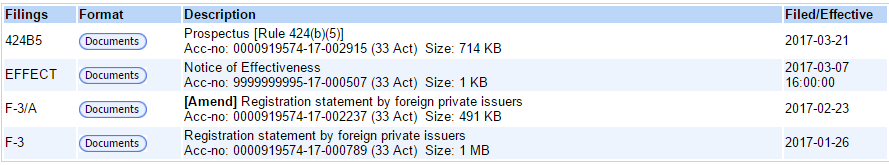
Besides the actual shelf registration statement, the company has to file a prospectus supplement within two days of whichever comes first, the offering being priced or the shelf registration being used. Also, just because a shelf registration is filed does not mean it can be used immediately — the registration needs to be declared effective after the SEC reviews the registration. This typically takes two to three weeks from when the registration statement is filed. When a shelf registration (or another registration statement) has become effective a form EFFECT will be posted. For example, here is a shelf registration, prospectus, and EFFECT for Diana Containerships (DCIX):
Disclaimer. No position in any stocks mentioned and I have no relationship with anyone mentioned in this post. This blog has a terms of use that is incorporated by reference into this post; you can find all my disclaimers and disclosures there as well.
Will the EFFECT always be filed before the prospectus supplement?
I’m not sure.